Enhancing Reproducibility in Distributed AI Training: Leveraging Checkpointing and Metadata Analytics
Reproducibility in distributed AI training is a crucial challenge due to several sources of uncertainty, including stragglers, data variability, and inherent randomness. Stragglers—slower processing nodes in a distributed system—can introduce timing discrepancies that affect the synchronization of model updates, leading to inconsistent states across training runs. Data variability, stemming from non-deterministic data shuffling and differing data partitions across nodes, can also lead to variations in model performance. Additionally, inherent randomness in algorithm initialization, such as random weight beginnings and stochastic processes like dropout, further compounds these challenges. Reproducibility in AI is pivotal for ensuring the credibility of AI-driven scientific findings, akin to how reproducibility underpins traditional scientific research.
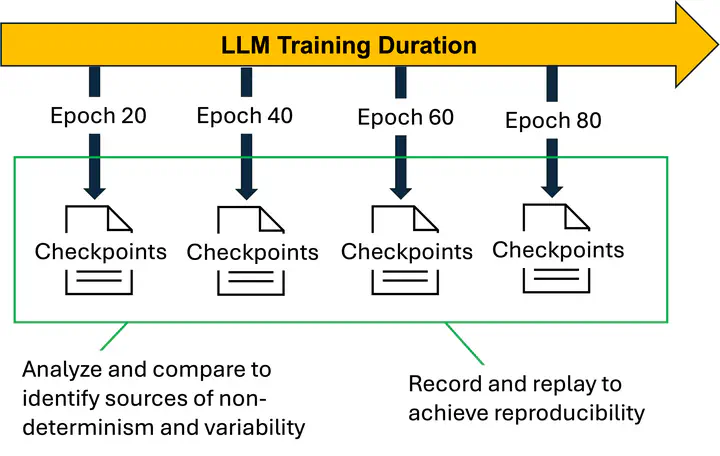
To enhance AI reproducibility, leveraging metadata analytics and visualization along with saved checkpoints offers a promising solution. Checkpointing in AI training is a pivotal technique that involves saving snapshots of a model and its parameters at regular intervals throughout the training process. This practice is essential for maintaining progress in the face of potential interruptions, such as hardware failures, and enables the resumption of training without having to restart from scratch. In the context of distributed AI training, checkpointing also provides a framework for analyzing and ensuring reproducibility, offering a means to systematically capture and review the training trajectory of models. Analyzing checkpoints can specifically help identify issues like stragglers, which are slower computing nodes in a distributed system that can impede synchronized progress. For example, by examining the time stamps and resource utilization data associated with each checkpoint, anomalies in processing time can be detected, revealing nodes that consistently lag behind others. This analysis enables teams to diagnose performance bottlenecks and optimize resource allocation across the distributed system, ensuring smoother and more consistent training runs. By combining checkpointing with metadata analytics, it becomes possible to pinpoint the exact training iterations where delays occur, thereby facilitating targeted investigations and solutions to improve overall system reproducibility and efficiency.
Workplan
The proposed work will include: 1) Setting up a checkpointing system within the distributed AI training framework to periodically save model states and metadata; 2) Designing a metadata analysis schema for populating model and system statistics from the saved checkpoints; 3) Conducting exploratory data analysis to identify patterns, anomalies, and sources of variability in the training process; 4) Creating visualization tools to represent metadata insights with collected statistics and patterns; 5) Using insights from metadata analytics and visualization to optimize resource distribution across the distributed system and mitigate straggler effects; and 6) Disseminating results and methodologies through academic papers, workshops, and open-source contributions.
- Topics:
ReproducibilityAIdistributed AIcheckpointmetadata analysis - Skills: C/C++, Python
- Difficulty: Medium
- Size: Large (350 hours)
- Mentors: Luanzheng "Lenny" Guo