RAG-ST: Retrieval-Augmented Generation for Spatial Transcriptomics
- Topics: bioinformatics, spatial transcriptomics, gene expression generation, retrieval-augmented generation, large models
- Skills:
- Programming Languages:
- Proficient in Python, and familiarity with machine learning libraries such as PyTorch.
- Data Analysis:
- Experience with spatial transcriptomics datasets and statistical modeling.
- Machine Learning:
- Understanding of vision models, retrieval-based systems, and MLP architectures.
- Bioinformatics Knowledge (preferred):
- Familiarity with scRNA-seq data integration and computational biology tools.
- Programming Languages:
- Difficulty: Advanced
- Size: Large (350 hours). Given the scope of integrating RAG models, building a robust database, and ensuring interpretable predictions, this project involves substantial computational and data preparation work.
- Mentors: Ziheng Duan (contact person)
Project Idea Description
Spatial transcriptomics (ST) is a revolutionary technology that provides spatially resolved gene expression measurements, enabling researchers to study cellular behaviour within tissues with unprecedented detail. This technology has transformed our understanding of complex biological systems, such as disease progression, tissue development, and cellular heterogeneity. However, the widespread adoption of ST is limited by its high cost and technical requirements.
Histology imaging, on the other hand, is far more accessible and cost-effective. If gene expression could be accurately predicted from histology images, it would enable researchers to leverage these abundant images for high-resolution biological insights without the need for expensive spatial transcriptomics experiments. This task has immense potential to democratize spatial transcriptomics research and significantly reduce costs.
Challenges in Current Approaches
Current methods for predicting gene expression from histology images typically involve:
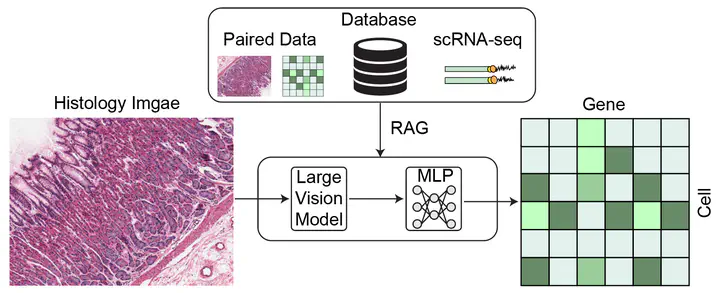
- Using large vision models to encode histology image patches into embeddings.
- Employing Multi-Layer Perceptrons (MLPs) to map these embeddings to gene expression profiles.
While these approaches have shown promise, they suffer from two critical limitations:
- Accuracy: The MLP-based mappings often fail to fully capture the biological complexity encoded in the histology images, leading to suboptimal predictions.
- Interpretability: These models act as black boxes, providing no insight into the underlying biological rationale for the predictions. Researchers cannot determine why a specific gene expression profile was generated, limiting trust and utility in biological contexts.
Project Motivation
To overcome these limitations, this project proposes a novel Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) framework for spatial transcriptomics. Instead of relying solely on black-box MLPs, RAG-ST will:
- Retrieve relevant examples from a curated database of paired histology images, scRNA-seq data, and gene expression profiles.
- Use these retrieved examples to inform and enhance the generation process, resulting in predictions that are both more accurate and biologically interpretable.
This approach not only grounds predictions in biologically meaningful data but also provides transparency by revealing which database entries influenced the results.
Project Objectives
- Database Construction:
- Curate a large and diverse database of histology images paired with scRNA-seq and gene expression data.
- Model Development:
- Develop a RAG framework combining vision-based encoders and retrieval-enhanced generation techniques.
- Incorporate interpretability mechanisms to link predicted gene expressions to retrieved examples.
- Evaluation and Benchmarking:
- Assess RAG-ST against state-of-the-art methods, focusing on accuracy, interpretability, and biological validity.
Project Deliverables
- Curated Database:
- A publicly available, well-documented database of histology images and gene expression profiles.
- RAG-ST Framework:
- An open-source Python implementation of the RAG-ST model, with retrieval, generation, and visualization tools.
- Benchmark Results:
- Comprehensive evaluations demonstrating the benefits of RAG-ST over conventional pipelines.
- Documentation and Tutorials:
- User-friendly guides to facilitate adoption by the spatial transcriptomics research community.
Impact
By integrating retrieval-augmented generation with large models, RAG-ST represents a paradigm shift in spatial transcriptomics. It offers a cost-effective, accurate, and interpretable solution for gene expression prediction, democratizing access to high-quality spatial transcriptomic insights and fostering advancements in biological research.