Smart Batching for Large Language Models
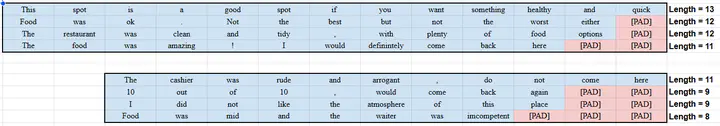
Sequence tokenization is a crucial step during Large Language Model training, fine-tuning, and inference. User prompts and training data are tokenized and zero-padded before being fed to the model in batches. This process allows models to interpret human language by breaking down complex sentences into simple token units that are numerically represented in a token set. However, the process of sequence padding for maintaining batch dimensions can introduce unnecessary overhead if batching is not properly done.
In this project, we introduce Smart Batching, where we dynamically batch sequences in a fine-tuning dataset by their respective lengths. With this method, we aim to minimize the amount of zero padding required during sequence batching, which can result in improved and efficient fine-tuning and inference speeds. We also analyze this method with other commonly used batching practices (Longest Sequence, Random Shuffling) on valuable metrics such as runtime and model accuracy.
Project Title
- Topics:
Large Language ModelsFine-TuningAITransformers - Skills: Python, Pytorch, Large Language Models
- Difficulty: Moderate
- Size: Large (350 hours)
- Mentor: [Daniel Wong]Daniel Wong, [Luanzheng “Lenny” Guo]Luanzheng "Lenny" Guo
Project Tasks and Milestones
- Implement an open source smart batching framework based on HuggingFace to allow for dynamically grouping sequences of similar token lengths into batches
- Analyze runtime, padding, and model accuracy with smart batching and other commonly used batching practices
- Apply smart batching with distributed fine-tuning and observe large language model outputs