NeuroHealth: AI-Powered Health Assistant
Project Description
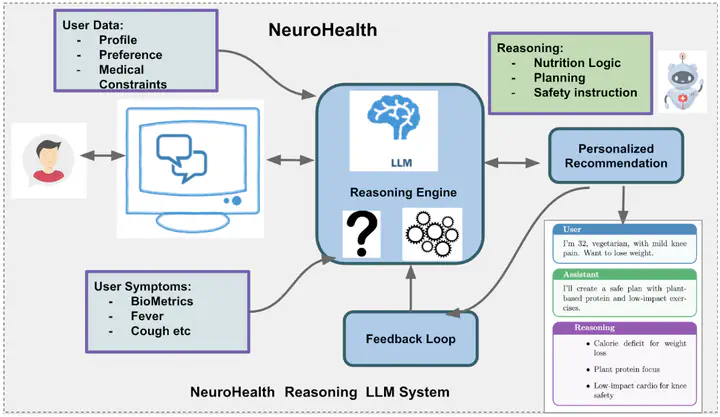
[NeuroHealth] Intelligent health assistance systems are increasingly essential for improving healthcare accessibility, patient engagement, and clinical decision support. In primary care and preventive medicine, AI assistants help users understand symptoms, schedule appropriate appointments, and receive preliminary health guidance. Telemedicine applications include triage support, appointment scheduling optimization, and patient education based on health inquiries. In chronic disease management, these systems provide medication reminders, lifestyle recommendations, and timely alerts for medical follow-ups. Healthcare navigation applications include finding appropriate specialists, understanding treatment options, and coordinating care across multiple providers. In wellness and preventive care, intelligent assistants enhance health literacy by delivering personalized health information, screening recommendations, and proactive health management strategies. By leveraging natural language understanding and medical knowledge integration, these systems enhance healthcare access, reduce unnecessary emergency visits, and empower users to make informed health decisions across diverse populations. Traditional health information systems often provide generic responses that fail to account for individual health contexts, medical history, and personal circumstances. Existing symptom checkers and health chatbots primarily rely on rule-based logic or simple decision trees, limiting their ability to understand nuanced health inquiries, reason about complex symptom patterns, or provide contextually appropriate guidance. These systems struggle with interpreting ambiguous descriptions, adapting to users’ health literacy levels, and generating personalized recommendations that account for individual medical constraints and preferences. To address these challenges, we propose NeuroHealth: AI-Powered Health Assistant, which leverages Large Language Models (LLMs) to create an intelligent conversational agent that synthesizes user health inquiries, symptom descriptions, and contextual information into actionable, personalized health guidance and appointment recommendations. By integrating LLM-based medical reasoning with structured clinical knowledge bases, NeuroHealth enhances symptom interpretation, appointment routing, and health education delivery. Unlike conventional systems that provide static responses from predetermined templates, NeuroHealth dynamically understands user intent, asks clarifying questions, assesses urgency levels, and generates appropriate recommendations—whether scheduling a doctor appointment, suggesting self-care measures, or directing users to emergency services. This fusion of LLM intelligence with validated medical knowledge enables a more accessible, adaptive, and helpful health assistance platform, bridging the gap between users seeking health information and appropriate medical care.
Project Objectives
Aligned with the vision of the 2026 Open Source Research Experience (OSRE), this project aims to develop an AI-Powered Health Assistant (NeuroHealth) to improve healthcare accessibility and patient engagement through intelligent conversational guidance. Healthcare systems face significant challenges in providing timely, personalized health information and connecting patients with appropriate care resources. Traditional symptom checkers and health information systems often deliver generic, rule-based responses that fail to account for individual contexts and struggle with natural language understanding. To address these limitations, this project will leverage Large Language Models (LLMs) to create an intelligent health assistant that understands user health inquiries, interprets symptom descriptions, assesses urgency, and provides personalized recommendations including doctor appointment suggestions, self-care guidance, and healthcare navigation support. The core challenge lies in designing NeuroHealth as a safe, accurate, and user-friendly system capable of natural conversation, medical knowledge retrieval, and appropriate response generation while maintaining clinical safety guardrails. Unlike conventional health chatbots that follow rigid conversation flows, NeuroHealth will reason over user inputs, ask clarifying questions, and dynamically adapt responses based on context, resulting in more helpful, accurate, and appropriate health assistance. Below is an outline of the methodologies and models that will be developed in this project.
Step 1: Data Collection & Knowledge Base Construction: Develop a comprehensive medical knowledge base integrating validated health information sources, symptom databases, condition descriptions, and appointment routing guidelines. Collect and curate conversational health inquiry datasets from public medical Q&A forums, symptom checker logs, and healthcare chatbot interactions to create training and evaluation data. Design structured representations for symptoms, conditions, urgency levels, and appointment recommendations to enable effective retrieval and reasoning. Extract common health inquiry patterns, symptom descriptions, and user intent categories to inform conversation flow design. Data sources can include public medical knowledge bases such as MedlinePlus, Mayo Clinic health information, clinical practice guidelines, and synthetic patient inquiry scenarios based on common healthcare use cases. Implement data validation mechanisms to ensure medical accuracy and clinical safety compliance.
Step 2: Model Development: Design and implement an LLM-based conversational health assistant that integrates medical knowledge retrieval with natural language understanding and generation. Develop a Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) architecture that grounds LLM responses in validated medical information sources, reducing hallucination risks and ensuring factual accuracy. Create prompt engineering strategies and reasoning frameworks that enable the system to: interpret symptom descriptions, assess urgency levels, ask appropriate clarifying questions, and generate personalized health guidance. Implement a multi-component architecture including: intent recognition, symptom extraction, urgency assessment, appointment recommendation generation, and response formatting modules. Develop clinical safety guardrails that detect high-risk scenarios requiring immediate medical attention and provide appropriate emergency guidance. Design conversation management strategies that maintain context across multi-turn dialogues and adapt to users’ health literacy levels. The baseline architecture can leverage state-of-the-art models such as GPT-4, Claude, or open-source alternatives like Llama, Qwen, combined with medical knowledge retrieval systems.
Step 3: Evaluation & Safety Validation: : Benchmark NeuroHealth against existing symptom checkers and health chatbots, evaluating on metrics including response accuracy, appropriateness of appointment recommendations, urgency assessment precision, and user satisfaction. Conduct human evaluation studies with healthcare professionals to assess clinical safety, response quality, and appropriateness of medical guidance. Perform adversarial testing to identify potential failure modes, unsafe responses, or inappropriate recommendations under edge cases. Conduct ablation studies to analyze the impact of retrieval-augmented generation, safety guardrails, and conversation management strategies on system performance. Evaluate system performance across diverse health inquiry types including acute symptoms, chronic condition management, preventive care questions, and healthcare navigation requests. Assess response quality across different user demographics and health literacy levels to ensure equitable access. Optimize inference efficiency and response latency for real-time conversational interaction across web and mobile platforms.
Project Deliverables
This project will deliver three components: model development, evaluation and validation, and interactive demonstration. The software implementing the NeuroHealth system will be hosted on GitHub as an open-access repository with comprehensive documentation, deployment guides, and API specifications. The evaluation results, including benchmark comparisons against existing systems, clinical safety assessments, and user study findings, will be published alongside the GitHub repository. An interactive demo showcasing the conversational interface, symptom interpretation capabilities, and appointment recommendation generation will be provided to illustrate real-world application scenarios.
NeuroHealth
- Topics: AI-Powered Health Assistant
- Skills: Proficiency in Python, Github, LLM
- Difficulty: Difficult
- Size: Large (350 hours)
- Mentor: Linsey Pang, Bin Dong
References:
- Large Language Models in Healthcare - Singhal et al., Nature 2023
- Med-PaLM: Large Language Models for Medical Question Answering - Singhal et al., arXiv 2022
- Capabilities of GPT-4 on Medical Challenge Problems - Nori et al., arXiv 2023
- MedlinePlus Medical Encyclopedia - https://medlineplus.gov/
- Clinical Practice Guidelines Database - https://www.guidelines.gov/