HistoMoE: A Histology-Guided Mixture-of-Experts Framework for Gene Expression Prediction
- Topics: computational pathology, spatial transcriptomics, gene expression prediction, mixture-of-experts, multimodal learning
- Skills:
- Programming Languages: Python; experience with PyTorch preferred
- Machine Learning: CNNs / vision encoders, mixture-of-experts, multimodal representation learning
- Data Analysis: handling large-scale histology image patches and gene expression matrices
- Bioinformatics Knowledge (preferred): familiarity with spatial transcriptomics or scRNA-seq data
- Difficulty: Advanced
- Size: Large (350 hours)
- Mentors: Ziheng Duan (contact person)
Project Idea Description
Histology imaging is one of the most widely available data modalities in biomedical research and clinical practice, capturing rich morphological information about tissues and disease states. In parallel, spatial transcriptomics (ST) technologies provide spatially resolved gene expression measurements, enabling unprecedented insights into tissue organization and cellular heterogeneity. However, the high cost and limited accessibility of ST experiments remain a major barrier to their widespread adoption.
Predicting gene expression directly from histology images offers a promising alternative, enabling molecular-level inference from routinely collected pathology data. Existing approaches typically rely on a single global model that maps image embeddings to gene expression profiles. While effective to some extent, these models struggle to capture the strong organ-, tissue-, and cancer-specific heterogeneity that underlies gene expression patterns.
This project proposes HistoMoE, a histology-guided mixture-of-experts (MoE) framework that explicitly models biological heterogeneity by learning specialized expert models for different cancer types or organs, and dynamically routing histology image patches to the most relevant experts.
Key Idea and Technical Approach
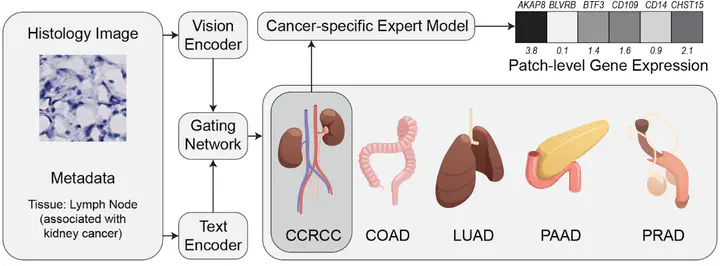
As illustrated in the figure above, HistoMoE integrates multiple data modalities and learning components:
Vision Encoder
Histology image patches are encoded into high-dimensional visual representations using a convolutional or transformer-based vision backbone.Text / Metadata Encoder
Sample-level metadata (e.g., tissue type, organ, disease context) is encoded using a lightweight text or embedding model.Gating Network
A gating network jointly considers image and metadata embeddings to infer routing weights over multiple cancer- or organ-specific expert models.Expert Models
Each expert specializes in modeling gene expression patterns for a specific biological context (e.g., CCRCC, COAD, LUAD), producing patch-level gene expression predictions.
By explicitly modeling biological structure through expert specialization, HistoMoE aims to improve both prediction accuracy and interpretability, allowing researchers to understand which biological experts drive each prediction.
Project Objectives
- Design and Implement the HistoMoE Framework
- Build a modular MoE architecture with pluggable vision encoders, gating networks, and expert models.
- Multimodal Routing and Expert Specialization
- Explore how image features and metadata jointly inform expert selection.
- Benchmarking and Evaluation
- Compare HistoMoE against single-model baselines on multiple cancer and organ-specific spatial transcriptomics datasets.
- Interpretability Analysis
- Analyze expert routing behavior to reveal biologically meaningful patterns.
Project Deliverables
- Open-Source HistoMoE Codebase
- Well-documented Python implementation with training, evaluation, and visualization tools.
- Benchmark Results
- Quantitative comparisons demonstrating improvements over non-expert baselines.
- Visualization and Analysis Tools
- Tools for inspecting expert usage, routing weights, and gene-level predictions.
- Documentation and Tutorials
- Clear instructions and examples to enable adoption by the research community.
Impact
HistoMoE introduces an expert-system perspective to histology-based gene expression prediction, bridging morphological and molecular representations through biologically informed specialization. By combining multimodal learning with mixture-of-experts modeling, this project advances the interpretability and accuracy of computational pathology methods and contributes toward scalable, cost-effective alternatives to spatial transcriptomics experiments.